Islamist Activist Asks Obama to Support Libyan AQ Group, Investigative Project on Terrorism, John Rossomando, March 18, 2016
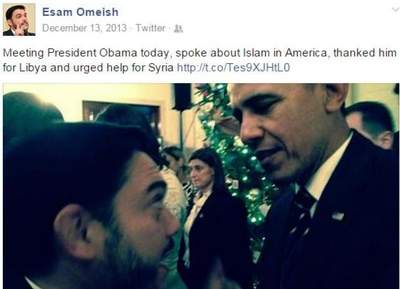
The revelation of his praise for Palestinians who chose “the jihad way” to liberation forced northern Virginia surgeon Esam Omeish to resign from a statewide immigration commission in 2007. But it hasn’t stopped him from enjoying red carpet treatment from Obama administration officials.
Omeish briefly drew national attention in 2007 when he was forced to resign from the Virginia immigration panel. The move resulted from Investigative Project on Terrorism (IPT) video showing him praising for Palestinians who chose the “jihad way” during a rally in 2000.
This was no slip of the tongue. At a different event two months earlier, Omeishcongratulated Palestinians who gave “up their lives for the sake of Allah and for the sake of Al-Aqsa. They have spearheaded the effort to bring victory upon the believers in Filastin, insha’allah [God willing]. They are spearing the effort to free the land of Filastin, all of Palestine, for the Muslims and for all the believing people in Allah.”
Nonetheless, high-ranking Obama administration officials engaged with him despite this and his praise for Hamas founder Sheikh Ahmed Yassin. They consulted with him on Libya and included him in other events aimed at engagement with the Muslim community and countering violent extremism.
Now, Omeish is hoping those contacts will help him persuade U.S. officials to change gears in Libya, shifting support from a secular political figure to one with links to al-Qaida. He spelled out those ambitions in a Feb. 29 letter addressed to President Obama posted on Omeish’s Facebook page.
It is co-signed by Emadeddin Z. Muntasser, secretary general of the Libyan American Public Affairs Council (LAPAC). Omeish is identified as the LAPAC president.
Before he was affiliated with the LAPAC, Muntasser was convicted in 2008 of failing to disclose connections between a charity he worked with and jihadist fundraising when he sought tax-exempt status for the charity.
Muntasser ran the Boston branch of the Al-Kifah Refugee Center, which is considered a precursor to al-Qaida, federal prosecutors have said. It was founded by Osama bin Laden’s mentor Abdullah Azzam. Under Muntasser’s leadership, Al-Kifah’s Boston office published a pro-jihad newsletter called Al-Hussam and distributed flyers indicating its support for jihadists fighting on the front lines in places such as Chechnya, Bosnia, Afghanistan and Algeria.
Muntasser’s charity, Care International, was “an outgrowth of and successor” to Al-Kifah, prosecutors say.
Omeish and Muntasser note in their letter that the U.S. has backed the “Libyan National Army,” led by Khalifa Hifter, a former general under dictator Muammar Gaddafi. That’s a bad idea, Omeish and Muntasser wrote, because “many in Libya believe [Hifter] has dictatorial aspirations …”
“He sounds like the Ahmed Chalabi of Libya,” said former Pentagon spokesman J.D. Gordon, a fellow at the Center for a Secure Free Society. “He wants America to fight his battles for him in order to gain the upper hand over his countrymen.”
However, the letter makes no mention of ties between the group Omeish endorses, the Revolutionary Council of Derna, and al-Qaida. Instead, he and Muntasser casts the group as an effective counter to ISIS because the council has “stripped [ISIS] from its social support. [ISIS]’s foreign presence and violent ways made them an evil that local Libyans themselves rejected and defeated” in Derna.
The council’s leaders included two men – Nasir Atiyah al-Akar and Salim Derbi –known to have had ties to al-Qaida.
After ISIS killed al-Akar, the Derna council eulogized him last June for his close ties to Abu Qatada, al-Qaida operative currently in Jordan. Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) reports from 2012 connect Akar to Abdulbasit Azzouz, who was al-Qaida leader Ayman al-Zawahiri’s man in Libya at the time. Azzouz allegedly was involved with the attack on the U.S. consulate and CIA annex in Benghazi that left U.S. Ambassador Stevens and three other Americans dead.
Derbi, also killed fighting ISIS, previously belonged to the al-Qaida linked Libyan Islamic Fighting Group (LIFG) and commanded the Abu Salim Martyrs Brigade, which also has al-Qaida ties.
Egypt’s Al-Alam Al-Youm refers to the Revolutionary Shura Council as “a branch of al-Qaida.”
Despite his ongoing connections to key White House decision-makers, Omeish appears headed for disappointment this time.
His letter is not likely to be read by the president’s national security team, a White House source told the Investigative Project on Terrorism (IPT). The U.S. is prepared to support a “Government of National Accord” that is being developed, the White House said in a statement.
However, the Obama administration repeatedly has involved Omeish in policy deliberations about Libya.
White House logs show that Omeish visited nine times since 2011, including a Dec. 13, 2013 visit in which he was photographed with President Obama.
Omeish’s encounter with the president came during the White House’s annual Christmas party, a White House spokesperson said. President Obama never conducts policy discussions at such public meetings, the source said.

Two photos appear on Omeish’s Facebook page showing him with U.N. Ambassador Samantha Power, widely considered an architect of the president’s Libya policy, where she advocated for military intervention. She notably helped draft PSD-11, a secret presidential directive that led to the U.S. supporting the Muslim Brotherhood in Libya among other places.
One photo shows Omeish meeting with Power in February 2012, when she worked as special assistant to the president and senior director for Multilateral Affairs and Human Rights at the National Security Council. The other photo posted the day Obama announced Power’s nomination as U.S. ambassador to the U.N. shows her standing next to Omeish.
White House officials thought enough of Omeish that they invited him to attend an April 2011 speech on Libya by President Obama at the White House. Omeish also attended the installation of Christopher Stevens, the late U.S. ambassador to Libya killed in the Sept. 11, 2012 Benghazi attack, and that of his successor, Deborah Jones, in 2013.
Omeish told The Washington Times following the Benghazi attack that he briefed Stevens before the ambassador began his duties in Tripoli.
Omeish and the Muslim Brotherhood
In addition to his comments about Palestinians and jihad, Omeish admits to prior personal involvement in the Muslim Brotherhood in the U.S. and served as president of the Muslim American Society, which has been described as the “overt arm” of the Brotherhood in America. His association with the Brotherhood likely dates back to his involvement in the Muslim Students Association (MSA) in the 1990s when he became the national organization’s president, which was founded by Brotherhood members in 1963.
Omeish endorsed Libya’s Muslim Brotherhood in a 2012 IRIN News article, stating that although it came in a distant second in Libya’s 2012 elections, it “may be able to provide a better platform and a more coherent agenda of national action.”
Libya’s Muslim Brotherhood subsequently failed to implement a coherent agenda and became deadlocked with its liberal rival, the National Forces Alliance, over establishing a working constitution.
Brotherhood members opposed building a strong Libyan military that could have helped rein in the militias that have since created havoc. Numerous militias tied to the Brotherhood have contributed to Libya’s instability. U.S. State Department officials contracted with the Brotherhood-linked February 17 Martyrs Brigade – a group that also had Al-Qaida ties – to provide security for the ill-fated U.S. consulate in Benghazi. A BBC report described the brigade as the best armed militia in eastern Libya. It additionally held al-Qaida sympathies, according to posts on its Facebook page. A State Department report called reliance on the February 17 militia in the case of an attack such as happened on Sept. 11, 2012 “misplaced.”
LAPAC is but one of an alphabet soup of groups that Omeish helped found as a result of the Arab Spring, aimed at affecting U.S. policy toward Libya.
This includes Libyan Emergency Task Force,(LETF), Libyan Americans for Human Rights, Libyan Council of North America (LCNA), Libyan American Organization, American Libyan Council, American Libyan Chamber of Commerce and Industry (ALCCI), Center for Libyan American Strategic Studies. Former Libyan Ambassador to the U.S. Ali Aujali appointed Omeish the official representative of the Libyan-American community, according to ALCCI’s old website.
LETF lobbied for the U.S. and the international community to establish a no-fly zone to keep Gaddafi from bombing rebellious cities in early 2011. Omeish’s LCNA worked to facilitate meetings between U.S. officials and Libyan rebels, including a meeting with John Kerry while he still was a U.S. senator. ALCCI works with the Libyan embassy in Washington to “certify and support trade relations between Libya and the United States.”
It remains to be seen whether the advice from Omeish and Muntasser will be ignored. But their gambit, publicly posting their letter urging the president to support Islamists, indicates a confidence generated by years of access and consultation. That raises a host of troubling questions.










Recent Comments