IDF Preparing for Arrival of ISIS on Syrian Border, Investigative Project on Terrorism, Yaakov Lappin, January 29, 2016
As conflict and mayhem continue to rage across Syria, the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) is preparing to encounter the threat of ISIS and al-Qaida forces right on its borders, and could encounter such threats in the coming months.
The preparations come as the Syrian civil war shows no sign of letting up. This is a conflict that has led to the violent deaths of 300,000 Syrians, and the displacement of more than 10 million others, 4.5 million of whom have fled the country.
Today, the IDF’s Military Intelligence Directorate views Syria as a former state that has broken apart into multiple ‘Syrias.’ The Assad regime controls barely 30 percent of Syria and is fully reliant on the foreign assistance of Russia, Hizballah, and Iran. Sunnis and Shi’ites wage daily war on one another.
It is worth examining the wider recent events in the multifaceted Syrian conflict, and place the IDF’s preparations in their broader regional perspective.
In Syria’s murderous kill-or-be-killed environment, Salafi-jihadist doctrines flourish, in the form of ISIS, which views Shi’ites (including the Assad regime and Hizballah) as infidels who must be destroyed.
ISIS cells have operated recently in Lebanon too, targeting Shi’ite Hizballah’s home turf of Dahiya in southern Beirut with two large bombings in November that claimed over 40 lives, while ISIS in Iraq continues to target Shi’ites.
Today, ISIS has between 30,000-50,000 members who are dedicated to expanding their caliphate and killing all those who disagree with their doctrine, including even fellow Sunni jihadi members of al-Qaida’s branch in Syria, the Al-Nusra Front, which has 8,000-12,000 members.
ISIS continues to use its territory in Syria and Iraq to plot major, mass-casualty terrorist attacks in Western cities. At the same time, its budgetary future looks uncertain, as oil funds have decreased significantly following allied air strikes on oil facilities. In the past year, 45 percent of ISIS’s $1.3 billion budget came from oil, far less than the oil revenue in 2014.
Unlike ISIS, al-Qaida believes in following a phased, slower plan in setting up a caliphate, and the two jihadist organizations have been at war with each other for more than two years in Syria.
Shi’ites led by Iran are fighting to stop the Salafi-jihadis’ spread. Under the command of Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC)-Quds Force unit commander, Qassem Suleimani, Iranian fighting forces and advisers moved into Syria. Iran has sustained more than 300 casualties there thus far.
Hizballah, too, is heavily involved in Syria’s battles, losing an estimated 1,300 fighters and sustaining 10,000 injuries – meaning more than half of its conscripted fighting force has been killed or wounded. Iran and its proxies are using the mayhem to try to spread their own influence in Syria.
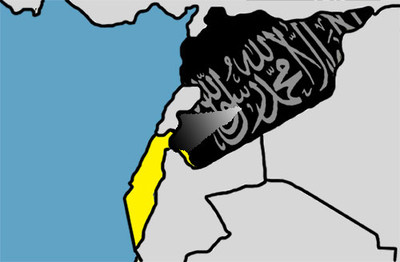
Near Israel’s border with Syria, the Al-Yarmouk Martyrs Battalions, which is affiliated with ISIS, has set up many posts.
An estimated 600 members of the group control a population of around 40,000 Syrians. Al-Yarmouk is at war with al-Qaida’s Jabhat Al-Nusra, which maintains a few thousand members in the Syrian Golan near Israel.
Jabhat Al-Nusra’s membership is mostly derived of local Syrians, who tend to be more hesitant to start a war with Israel that would result in their areas, and relatives, being badly affected. Yet 10 to 15 percent of its membership comes from abroad, and have no commitment to the area. These foreign fighters have no qualms about precipitating attacks on Israel. At the moment, however, Jabhat Al-Nusra is bogged down by its fight with Al-Yarmouk.
ISIS has officially put Israel in its sights, and its leader, Abu Bakr Al-Baghdadi, declared his intention at the end of December to attack Israel.
The IDF is taking the threat seriously and is preparing for a range of possible attacks, including strategic terror attacks, cross-border raids, the sending of bomb-laden armored vehicles into Israel, and rocket, missile, small-arms, and mortar fire on the Israeli Golan Heights.
One possibility is that the heavily armed Al-Yarmouk group, which is facing the southern Golan Heights, might follow an Islamic State directive to attack Israel.
In 2014, Al-Yarmouk became an ISIS representative, swearing allegiance to it, though it is not fully subordinate to it.
Al-Yarmouk’s late leader, known as Al Khal (“the uncle”), was killed in November in an attack by Jabhat Al-Nusra. Before his violent end, Al Khal only partially committed himself to ISIS, and turned down ISIS requests to send fighters to Iraq.
Al-Yarmouk’s response to Jabhat Al-Nusra’s attacks came in December, when it assassinated a Jabhat Al-Nusra commander in his armored vehicle, just 400 meters from the Israeli border.
Al-Yarmouk subscribes to the Salafi jihadist ideology and has shoulder-held missiles, tanks, and other weapons looted during raids on the Assad regime military bases.
But Israel is also preparing for the possibility of encountering ISIS itself, not just an affiliate group.
ISIS proper is currently situated 40 kilometers from the Israeli border in southern Syria. One possibility is that Russian airstrikes will cause ISIS forces to ricochet southwards, towards Israel.
The IDF is gathering intelligence on all armed groups near its border, exhausting many resources to assess their capabilities, and intentions.
Israel watched as Shi’ite Hizballah came from Lebanon to block Sunni jihadist advances towards Lebanon in recent months, and as Russian airstrikes blocked the advance of the rebels northwards, to Damascus.
The IDF remains in a heightened state of alert along the Syrian border, though it is also working to avoid the creation of easy targets for the array of predatory forces on the other side.
As part of its preparations, the IDF’s Northern Command has given more autonomy to regional field commanders to enable faster responses to surprise attacks by reducing the initial chain of command during emergencies.
Inter-branch cooperation between intelligence, ground forces, and the air force has also been tightened.
Additionally, the IDF has fortified its border fence with Syria, adding electronic sensors to better be able to detect and respond to a potential attack in time.
The underlying assumption within military circles is that, sooner or later, ISIS will turn its guns on Israel, and the IDF does not intend to be caught off guard when that happens.













Recent Comments